Diopsys® NOVA™ Vision Testing System
For several years now, tremendous progress has been made in glaucoma management and medical retina through Diopsys® NOVA™ Vision Testing System.
Making electrophysiologic testing accessible and efficient in the clinic.
Electrophysiologic testing is usually associated with a time-consuming and uncomfortable test in which the graphs are difficult to interpret. Therefore testing has been performed almost exclusively by universities for decades.
However, Diopsys has developed highly conductive skin electrodes that allow simple and fast testing without any discomfort or corneal risk for the patient. In addition, a normative database has been established and qualitative parameters for the obtained curve were developed in order to make interpretation of the result very easy for the clinician.
Glaucoma
As a clinician you want to rapidly see who needs your attention. Stop wasting your time on stable cases. This is why you need to perform Diopsys’ pERG for your glaucoma patients!
We need to think in terms of cell disease rather than cell death.
That’s exactly what pERG allows you to do.
Where visual field testing and OCT provide a report on the cumulative functional resp. structural damage that has developed over the years, the analysis with Diopsys' pattern ERG (pERG) provides an immediate picture of current disease activity. This saves a lot of time as you no longer need waiting months or years to detect (further) progression on visual field or OCT.
Obtaining Diopsys’ pERG will help you guide glaucoma management in a very wide range of clinical situations, such as:
- To find out if the current level of IOP is causing ganglion cell damage
- Verify whether the obtained IOP reduction after treatment is sufficient
- Determine whether an occludable anterior chamber angle (PACS) requires treatment
- Verify whether the treatment of an occludable anterior chamber angle (PACS) has given a satisfactory result
- Distinguish normals from preperimetric glaucoma cases in patients with a suspicious optic disc without convincing visual field and / or OCT results.
- Detect glaucoma in cases with tilted disc or high myopia
- Distinguish normals from glaucoma cases in patients with varying or unreliable performance of visual field tests
- Detection of persistent ganglion cell dysfunction in existing visual field defects despite obtaining (apparently) sufficient IOP reduction.
- Evaluation of complaints of poor visual quality
pERG normalizes within 3 months after treatment, which is only a fraction of the time needed to detect further visual field or OCT progression. This dramatic increase of diagnostic efficacy allows you to save chair time for those who really need it.
The implementation of Diopsys' pERG makes it possible to obtain an analysis of the current ganglion cell function for all degrees of visual field defects. Normalisation of ganglion cell function is obtained within 3 months of elimination of the mechanism of damage. This allows you to assess the actual ganglion cell function and permits to verify within a very short time frame if the treatment is producing sufficient results.
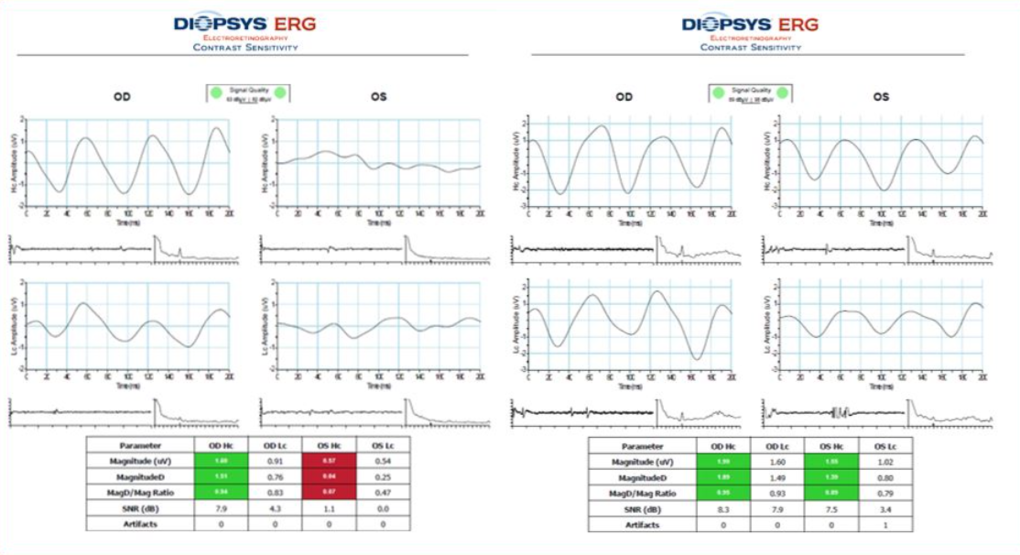
Example of pERG improvement from pre-treatment (left) to 3 months post treatment (right)
Transition from time domain to frequency domain has transformed pERG into a clinically undispensable tool.
It is well established that RGC dysfunction and subsequent apoptosis precede axonal loss. Thus pattern ERG (pERG) will detect early disease. However, obtaining a transient pERG has several practical and methodological draw-backs, limiting its use to university clinics and specialised labs. In contrast to this old method the newer steady state pERG uses a high frequency stimulus, producing a sinusoidal waveform which is mathematically analysed and compared to a normative database. The confidence intervals in the print-out deliver a result that can be easily and rapidly interpreted by the clinician.
In this article, Dr Good (UK) gives an overview on the use of pERG in glaucoma management.
In this poster presented at ARVO by A. Tirsi et al. (New York), a clear separation of parameters is demonstrated between the converting and non-converting group in glaucoma suspect.
Via this link you can watch a video in which Mark Latina (Tufts university school of medicine) gives an introduction to Diopsys' pERG technology.
This link will take you to the Diopsys website, where you will find more information about the applications of Diopsys® NOVA™ Vision Testing System in the field of glaucoma management and medical retina.
If you wish to contact cVision, distributor of Diopsys® NOVA™ Vision Testing System in Belgium, send us an email : sales@cvision.be
Retina
Struggling to find out which diabetic patients will progress? Overbooked schedules with moderate disease cases that turned out to be stable?
As a clinician you want to rapidly detect who needs your care. This is why you need to perform Diopsys’ full field flicker ERG in retinal disease!
Detecting diseased - but still viable - cells allows for intervention aiming for functional recovery
Visual activity provides us of a measure of central foveal function in a 100% contrast setting. However this measure is subjective and even when half of the fovea is obscured or non-functioning, patients may still achieve 10/10 vision. Visual field testing is another way to measure visual function but requires patient coöperation and may suffer considerable inter-test variability.
The full field flicker ERG (ffERG) is a light induced visual response and the only diagnostic test that allows the clinician to obtain an objective assessment of of cone and bipolar function over the entire retina.
ffERG provides an objective measure of retinal function improvement after treatment.
ffERG is easy to use, non-invasive, fast and gives a standard report that is very simple to interpret: equally spaced high peaks on the magnitude graphs and closely packed lines pointing in around 5 o’clock in the lower right quadrant of the Mag/Phase plot indicate good cone function. ffERG results are reliable even when media opacities are present.
![]()
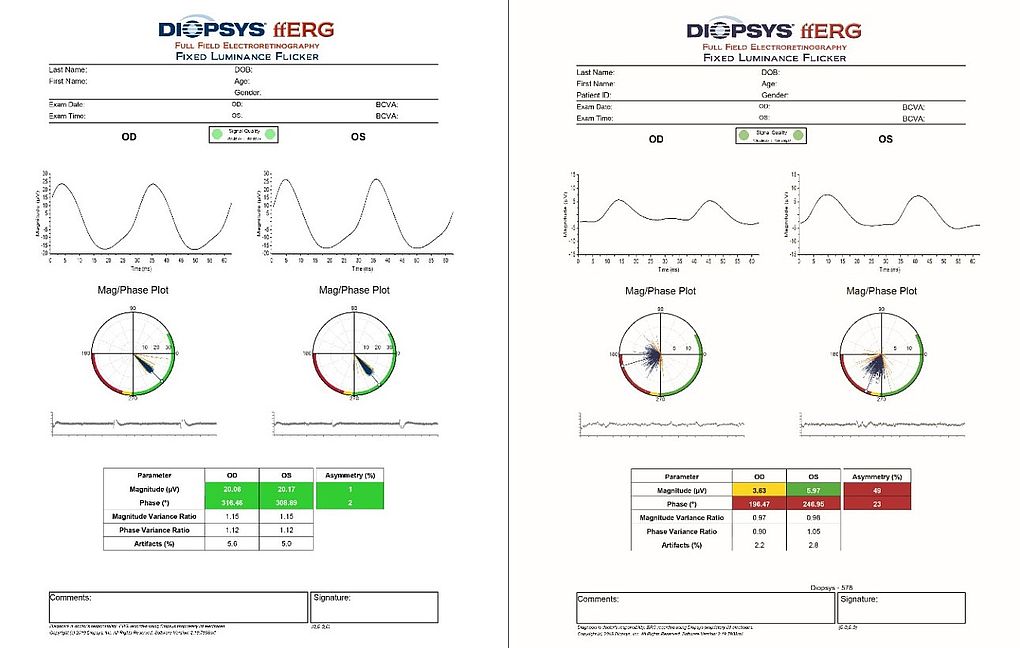
As an objective, reliable and quantitative measurement, flicker ERG can be used in the detection, evaluation and follow-up of conditions that can cause generalized retinal dysfunction.
- Detection of retinal dysfunction before diabetic retinopathy becomes clinically visible on fundoscopy
- Detection of retinal dysfunction before CME is visible on OCT
- Detection of ischemia
- Follow-up of function recovery after treatment
- Prediction of neovascularisation in CRVO
- assessment of retinal function in cases of dense cataract
- assessment of visual complaints not explained by anatomical findings
Transition from time domain to frequency domain has transformed pERG into a clinically undispensable tool.
Full field ERG (ffERG) has evolved from the earlier txime-domain to a frequency domain analysis, using a flash stimulus of a frequency higher than the refresh rate of rod photoreceptors, thus measuring cone and bipolar cell function. Although cone density is highest in the fovea, the fovea contains only 3.3% of all cones that are distributed throughout the retina. ffERG measures the stimulation of the entire retina, providing a measure of global retinal function. It serves as a biomarker to demonstrate functional changes independent of structural tests (OCT) and can detect loss of function before structural changes are detectable.
- ffERG has proven to be a successful tool in the early diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy1,2: disease related damage can be detected before fundus changes become clinically apparent.
- As vasodilation capacity of retinal vessels of diabetics in response to light is reduced directly proportional to the degree of retinopathy, ffERG provides an evaluation of the neurovascular coupling response to light stimuli1.
- ERG predicts progression of diabetic retinopathy1
- pERG and ffERG are relevant for the evaluation and management of diabetic retinopathy with and without DME
- In non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy, reduced retinal function in presence of 1.0 BCVA can indicate peripheral capillary dropout
- Flicker phase is negatively correlated with the ischemic index as measured during ultra-widefield fluo-angiography2
- In CRVO, ERG findings predict neovascularisation (94%) better than fluo-angiography (80%)3
For a case study of CRVO, follow this link
Watch this video for an overview of the use of ffERG in the ophthalmic practice
This link will take you to the Diopsys website, where you will find more information about the applications of Diopsys® NOVA™ Vision Testing System in the field of glaucoma management and medical retina.
If you wish to contact cVision, distributor of Diopsys® NOVA™ Vision Testing System in Belgium, send us an email : sales@cvision.be
1 Role of electrophysiology in the early diagnosis and follow-up of diabetic retinopathy. N Pescosolido et al. Journal of Diabetes Research Vol.2015, Article ID 319692
2 Reproducibility of fixed-luminance and multi-luminance flicker electroretinography in patients with diabetic retinopathy using an office-based testing paradigm. J. Wroblewski et al., Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology, 2019
3 fluorescein angiography versus ERG for predicting the prognosis in central retinal vein occlusion. Larsson J et al, Acta Ophth Scandinavia, 1998